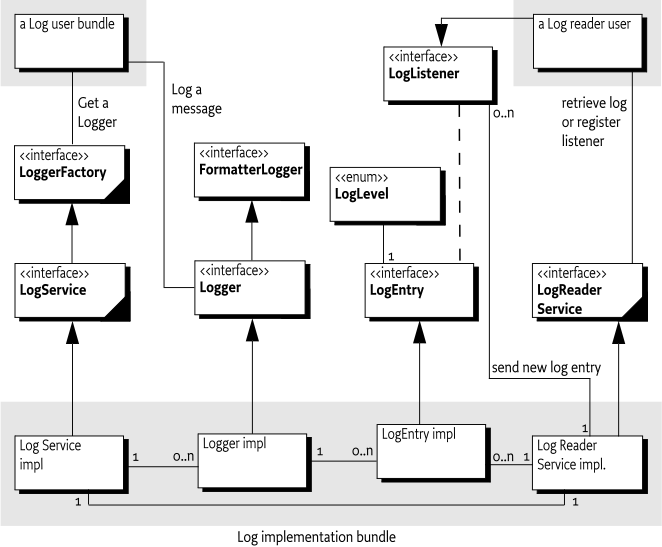
The Log Service provides a general purpose message logger for the OSGi framework. It consists of several services: a service for obtaining Loggers to log information and other services for retrieving current or previously recorded log information.
This specification defines the methods and semantics of interfaces which bundle developers can use to log entries and to retrieve log entries.
Bundles can use the Logger Factory to log information for the Operator. Other bundles, oriented toward management of the environment, can use the [3] Log Stream Provider Service or Log Reader Service to retrieve Log Entry objects that were recorded recently or to receive Log Entry objects as they are logged by other bundles.
-
Logger - An interface that allows a bundle to log information, including a message, a level, an exception, and a
ServiceReferenceobject. -
LoggerFactory - The service interface that allows a bundle to obtain a Logger. A Logger is named and associated with a
Bundleobject. -
LogService - The legacy service interface that allows a bundle to log information, including a message, a level, an exception, a
ServiceReferenceobject, and aBundleobject. The methods of this service are deprecated and it is recommended to use LoggerFactory and Loggers instead. -
LogEntry - An interface that allows access to a log entry in the log. It includes all the information that can be logged through the Logger as well as a time stamp, a sequence number, thread information, and location information.
-
LogReaderService - A service interface that allows access to a list of recent
LogEntryobjects, and allows the registration of aLogListenerobject that receivesLogEntryobjects as they are created. -
LogListener - The interface for the listener to
LogEntryobjects. Must be registered with the Log Reader Service. -
LoggerContext - An interface that allows the configuration of effective logging levels for a Bundle. The configuration can be set in Configuration Admin and via method calls.
-
LoggerAdmin - A service interface that allows for the configuration of logging. The service provides access to Logger Context objects.
The Logger interface allows bundle developers to log messages that can be distributed to other bundles, which in turn can forward the logged entries to a file system, remote system, or some other destination. It is inspired by the ideas used in [1] SLF4J.
The Logger interface allows the bundle developer
to:
-
Specify a message, message parameters, and an exception to be logged.
-
Define the log level representing the severity of the message being logged. If the effective log level for the Logger does not imply the requested log level, then the logging request is ignored. See Effective Log Level.
-
Specify the Service associated with the message being logged.
-
Query if a log level is effective.
By obtaining a Logger object from the LoggerFactory service, a bundle can start logging messages to the Log Service by calling one of the Logger methods.
The Logger interface defines several methods for each of the defined LogLevels.
Table 101.1 Log Levels
| Log Level | Descriptions |
|---|---|
|
This log level is used for information that must always be logged. |
|
|
This log level is used for information about an error situation. |
|
|
This log level is used for information about a failure or unwanted situation that is not blocking. |
|
|
This log level is used for information about normal operation. |
|
|
This log level is used for detailed output for debugging operations. |
|
|
This log level is used for large volume of output for tracing operations. |
Many of the Logger methods take a
message format string and message parameters which are formatted together
to create the log message. In the format string, use a left curly bracket
('{' \u007B) followed by a right curly bracket ('}'
\u007D) as a place holder for a message parameter:
"{}". If you need to use the literal "{}" in the
formatted message, precede the place holder with a reverse solidus
('\' \u005C): "\\{}". If you need to place a
backslash before the place holder, precede the reverse solidus with a
reverse solidus: "\\\\{}".
You can also add a Throwable and/or ServiceReference to the
generated LogEntry by passing them to the logging methods as
additional arguments to the Logger method. If the last
argument is a Throwable or a ServiceReference, it is added to the
generated LogEntry and then, if the next to last argument is a
ServiceReference or Throwable and not the same type as the last argument,
it is also added to the generated LogEntry. These
arguments will not be used as message parameters. For example:
logger.info("Found service {}.", serviceReference, serviceReference);
logger.warn("Something named {} happened.", name, serviceReference, throwable);
logger.error("Failed.", exception);The following example code records error conditions as log messages.
try (InputStream in = Files.newInputStream(myFile)) {
int b;
while ((b = in.read()) != -1 ) {
...
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("Cannot access file {}", myFile, e);
}Notice that in addition to the error message, the exception itself is also logged. Providing this information can significantly simplify problem determination by the Operator.
Sometimes message parameters can be expensive to compute, so
avoiding computation is important if the log level is not effective. This
can be done using either an if block or a LoggerConsumer. The
latter is convenient as a lambda expression. For example, both of the
following examples avoid computation if the log level is not
effective.
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Max {}", Collections.max(processing));
}logger.info(l -> l.info("Max {}", Collections.max(processing)));The latter example only calls the lambda expression if the log level is effective.
Logger
objects can be obtained from the LoggerFactory
service. Loggers are named. Logger names should be in the form of a fully
qualified Java class names with segments separated by full stop ('.'
\u002E). For example:
com.foo.BarLogger names form a hierarchy. A logger name is said to be an ancestor of another logger name if the logger name followed by a full stop ('.' \u002E) is a prefix of the descendant logger name. The root logger name (ROOT_LOGGER_NAME) is the top ancestor of the logger name hierarchy. For example:
com.foo.Bar
com.foo
com
ROOTNormally the name of the class which is doing the logging is used as
the logger name. There are Logger Factory methods which take
Class objects to simplify this.
Logger logger = loggerFactory.getLogger(Bar.class);The LoggerFactory service can be used to obtain two types of Logger
objects: Logger and FormatterLogger.
The Logger
object uses SLF4J-style ("{}") place holders for message
formatting. The FormatterLogger object use printf-style place holders from
java.util.Formatter for message formatting.
FormatterLogger logger = loggerFactory.getLogger(Bar.class,
FormatterLogger.class);
logger.error("Cannot access file %s", myFile);Some bundles, such as the Service Component Runtime implementation, may need to log on behalf of other bundles. The getLogger(Bundle,String,Class) method can be used to obtain a Logger object associated with the specified bundle.
Logger logger = loggerFactory.getLogger(componentBundle,
componentImplClassName,
Logger.class);As long as the LoggerFactory service, from which the Logger is obtained, is active, that is, the LoggerFactory service has not been unregistered, then the Logger is valid and can be used to log. However, once the LoggerFactory service has been unregistered, then Logger objects obtained from the LoggerFactory service must enter a "no-op" state where no log level is effective and no logging occurs.
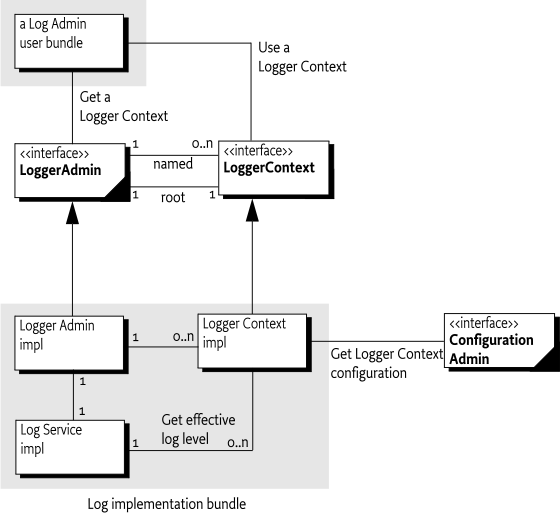
A Logger Admin service is defined which allows for the configuration of Loggers.
The LoggerAdmin service can be used to obtain the LoggerContext for a bundle. Each bundle may have its own named LoggerContext based upon its bundle symbolic name, bundle version, and bundle location. There is also a root LoggerContext from which all named LoggerContexts inherit. The root LoggerContext has no name.
The LoggerAdmin service is associated with the LoggerFactory service it administrates via the LOG_SERVICE_ID service property whose value is a Long containing the service.id of the LoggerFactory service.
A Logger implementation must locate the LoggerContext for the bundle to determine the effective log level of the Logger when a log method is called. See Effective Log Level. The best matching name for the LoggerContext is the longest name, which has a non-empty LoggerContext, according to the following syntax:
name ::= symbolic-name ( ’|’ version ( ’|’ location )? )?The version must be formatted canonically, that is, according to the
toString() method of the Version class. So the
LoggerContext for a bundle is searched for using the following
names in the given order:
<symbolic-name>|<version>|<location>
<symbolic-name>|<version>
<symbolic-name>The search stops at the first non-empty LoggerContext. If no non-empty LoggerContext is found using the above search order, the LoggerContext with the symbolic name of the bundle must be used.
This allows a bundle to have no LoggerContext configured. In this case it will use the root LoggerContext's configuration. It also allows a bundle to be configured based upon bundle symbolic name, bundle symbolic name and bundle version or even bundle symbolic name, bundle version, and bundle location. The latter forms may be of interest if there are multiple versions of a bundle installed.
LoggerContexts can be configured using the getLogLevels() and setLogLevels(Map) methods of the LoggerContext. Logger names, including the root logger name (ROOT_LOGGER_NAME), can be configured to a specific log level.
Any change to the configuration of a LoggerContext must be effective immediately for all loggers that would rely upon the configuration of the LoggerContext. Changes to the configuration of a LoggerContext via the setLogLevels(Map) method are not persisted.
The configured log levels for a LoggerContext can be set by both the setLogLevels(Map) method and by configuration information in Configuration Admin, if Configuration Admin is present. The configured log levels for a LoggerContext are based upon the last technique used to update the configured log levels.
If Configuration Admin is present, LoggerContext configuration information in Configuration Admin must be used. This allows external LoggerContext configuration such as via [2] Configurator. The name of the LoggerContext is mapped to a Configuration Admin targeted PID as follows:
-
The root LoggerContext, which has no name, is mapped to the PID LOGGER_CONTEXT_PID.
-
A named LoggerContext is mapped to a targeted PID by prefixing the LoggerContext's name with LOGGER_CONTEXT_PID followed by vertical line (
'|' \u007c). For example, the LoggerContext namedcom.foo.baris mapped to the targeted PIDorg.osgi.service.log.admin|com.foo.bar.
In the Configuration for the targeted PID, the dictionary keys are
Logger
names having a key type of String, and the values are the
names of the LogLevel values having a value type of
String. If the Configuration contains any key/value pairs
whose value is not the name of a LogLevel value,
that key/value pair must be ignored when setting the configuration into
the LoggerContext.
Any change to the Configuration for a LoggerContext must be set into the LoggerContext as soon as possible. Since notification of Configuration changes happen asynchronously, it may take a brief period of time before Configuration changes can be made effective.
This section is not meant to require that a Log Service implementation must require Configuration Admin. But if Configuration Admin is present, the Configurations must be used to set the log levels in the mapped LoggerContexts.
Once the LoggerContext for the logging bundle is determined, the effective log level for the Logger is found using the getEffectiveLogLevel(String) method:
-
If the logger name is configured with a log level, return the configured log level.
-
For each ancestor logger name of the logger name, if the ancestor logger name is configured with a log level, return the configured log level.
-
If the LoggerContext is named, return the result of calling the getEffectiveLogLevel(String) method on the root LoggerContext with the logger name.
-
If the LoggerContext is the root Logger Context, return the default log level for the root LoggerContext.
The default log level for the root LoggerContext can be set by the framework launch property LOGGER_CONTEXT_DEFAULT_LOGLEVEL. The value of this property must be the name of the one of the LogLevel values. If not specified, or the specified value is not the name of the one of the LogLevel values, the default log level of the root LoggerContext is WARN.
The Log Reader Service maintains a list of LogEntry objects called the log. The Log Reader Service is a service that bundle developers can use to retrieve information contained in this log, and receive notifications about LogEntry objects when they are created through the Log Service.
The size of the log is implementation-specific, and it determines how far into the past the log entries go.
The LogReaderService interface defines the following methods:
-
getLog() - This method retrieves past log entries as an enumeration with the most recent entry first.
-
addLogListener(LogListener) - This method is used to subscribe to the Log Reader Service in order to receive log messages as they occur. Unlike the previously recorded log entries, all log messages must be sent to subscribers of the Log Reader Service as they are recorded.
After a subscription to the Log Reader Service has been started, the subscriber's logged(LogEntry) method must be called with a LogEntry object for the message each time a message is logged.
-
removeLogListener(LogListener) - This method is used to unsubscribe the LogListener from the Log Reader Service.
The LogListener interface defines the following method:
-
logged(LogEntry) - This method is called for each LogEntry object created.
The delivery of LogEntry objects to the LogListener object should be done asynchronously.
The LogEntry interface abstracts a log entry. It is a record of the information that was passed when an event was logged as well as information captured at the time the event was logged. The LogEntry interface defines these methods to retrieve this information.
-
getBundle() - This method returns the Bundle object associated with the Logger used to create the log entry.
-
getException() - This method returns the logged exception, if any. In some implementations, the returned exception may not be the original exception object. To avoid references to a bundle-defined exception class, thus preventing an uninstalled bundle from being garbage collected, the Log Service may return an exception object of an implementation defined Throwable subclass. This object will attempt to return as much information as possible, such as the message and stack trace, from the original exception object .
-
getLoggerName() - This name of the Logger used to create the log entry.
-
getLogLevel() - This method returns the LogLevel.
-
getMessage() - This method returns the formatted message.
-
getServiceReference() - This method returns the logged
ServiceReference, if any. -
getTime() - This method returns the time that the log entry was created.
-
getSequence() - This method returns a sequence number which increases for each created log entry.
-
getThreadInfo() - This method returns information about the thread that created the log entry.
-
getLocation() - This method returns a
StackTraceElementabout the caller that created the log entry.
Implementations of a Log Service must log Framework-generated events and map the information to LogEntry objects in a consistent way. Framework events must be treated exactly the same as other logged events and distributed to all LogListener objects that are associated with the Log Reader Service. Additionally, if the Event Admin service is present, implementations of a Log Service must map LogEntry objects to events in Event Admin. The following sections define these mappings.
A Bundle Event is mapped to a LogEntry object according to the following table.
Table 101.2 Mapping of Bundle Events to Log Entries
| Log Entry method | Information about Bundle Event |
|---|---|
| getLoggerName() |
The logger name
|
| getLogLevel() | |
| getBundle() |
Identifies the bundle to which the event happened.
In other words, it identifies the bundle that was installed,
started, stopped, updated, or uninstalled. This identification
is obtained by calling |
| getException() |
|
| getServiceReference() |
|
| getMessage() |
The message depends on the event type:
|
A Service Event is mapped to a LogEntry object
according to the following table.
Table 101.3 Mapping of Service Events to Log Entries
| Log Entry method | Information about Service Event |
|---|---|
| getLoggerName() |
The logger name
|
| getLogLevel() |
INFO, except for
|
| getBundle() |
Identifies the bundle that registered the service
associated with this event. It is obtained by calling
|
| getException() |
|
| getServiceReference() |
Identifies a reference to the service associated
with the event. It is obtained by calling
|
| getMessage() |
This message depends on the actual event type. The messages are mapped as follows:
|
A Framework Event is mapped to a LogEntry object according to the following table.
Table 101.4 Mapping of Framework Event to Log Entries
| Log Entry method | Information about Framework Event |
|---|---|
| getLoggerName() |
The logger name
|
| getLogLevel() |
INFO, except for
|
| getBundle() |
Identifies the bundle associated with the event.
This may be the system bundle. It is obtained by calling
|
| getException() |
Identifies the exception associated with the error.
This will be null for event types other than
|
| getServiceReference() |
|
| getMessage() |
This message depends on the actual event type. The messages are mapped as follows:
|
Log entries must be mapped into events by the Log Service implementation and delivered asynchronously to the Event Admin service (if present). The following event topics are used based upon the log level of the log entry:
Table 101.5 Event Topics
| Event Topic | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
When the log level is AUDIT. |
|
|
When the log level is ERROR. |
|
|
When the log level is WARN. |
|
|
When the log level is INFO. |
|
|
When the log level is DEBUG. |
|
|
When the log level is TRACE. |
The properties of a log event are:
-
bundle.id- (Long) The source bundle's id. -
bundle.symbolicName- (String) The source bundle's symbolic name. Only set if notnull. -
bundle- (Bundle) The source bundle. -
log.level- (Integer) The integer log level. -
log.loggername- (String) The logger name. -
log.threadinfo- (String) The thread information for the thread creating the log entry. -
log.loglevel- (LogLevel) The log level. -
message- (String) The log message. -
timestamp- (Long) The log entry's timestamp. -
log.entry - (
LogEntry) The LogEntry object.
If the log entry has an associated Exception:
-
exception.class- (String) The fully-qualified class name of the attached exception. Only set if thegetExceptionmethod returns a non-nullvalue. -
exception.message- (String) The message of the attached Exception. Only set if the Exception message is notnull. -
exception- (Throwable) The Exception returned by thegetExceptionmethod.
If the getServiceReference method returns a non-
null value:
-
service- (ServiceReference) The result of thegetServiceReferencemethod. -
service.id- (Long) The id of the service. -
service.pid- (String) The service's persistent identity. Only set if theservice.pidservice property is notnull. -
service.objectClass- (String[]) The object class of the service object.
The members of the LogService interface are deprecated. Its log
methods can still be used by bundles. These log methods are
now specified to log to the Logger with the logger name
"LogService.<bsn>" where <bsn> is
the Bundle Symbolic Name of the bundle which obtained the LogService object.
This allows legacy logging to be configured as specified above.
Furthermore, the integer log level values used with the log
methods are mapped to the new LogLevels as
follows:
The specified integer log level value is stored in the generated LogEntry to be returned by getLevel().
The implementation of this specification must use a single service registration using both the LogService and LoggerFactory service names since both service names represent the same log and since the LogService type extends the LoggerFactory type.
The bundle providing the LoggerFactory and
LogService
service must provide a capability in the osgi.service
namespace representing this service. This capability must also declare a
uses constraint for the org.osgi.service.log package:
Provide-Capability: osgi.service;
objectClass:List<String>=
"org.osgi.service.log.LoggerFactory,org.osgi.service.log.LogService";
uses:="org.osgi.service.log" The bundle providing the LogReaderService
service must provide a capability in the osgi.service
namespace representing this service. This capability must also declare a
uses constraint for the org.osgi.service.log package:
Provide-Capability: osgi.service;
objectClass:List<String>="org.osgi.service.log.LogReaderService";
uses:="org.osgi.service.log" The bundle providing the LoggerAdmin
service must provide a capability in the osgi.service
namespace representing this service. This capability must also declare a
uses constraint for the org.osgi.service.log.admin package:
Provide-Capability: osgi.service;
objectClass:List<String>="org.osgi.service.log.admin.LoggerAdmin";
uses:="org.osgi.service.log.admin" These capabilities must follow the rules defined for the
osgi.service Namespace.
The Log Service specification should only be implemented by trusted
bundles. These bundles require
ServicePermission[LoggerFactory|LogReaderService|LoggerAdmin|LogService,
REGISTER] and
ServicePermission[ConfigurationAdmin|EventAdmin, GET].
Virtually all bundles should get
ServicePermission[LoggerFactory|LogService, GET] so they can
log.
Only trusted bundles who must be able to access log entries should
be assigned ServicePermission[LogReaderService, GET].
Only trusted bundles who must be able to change log configuration
should be assigned ServicePermission[LogAdmin, GET].
Log Service Package Version 1.5.
Bundles wishing to use this package must list the package in the Import-Package header of the bundle's manifest. This package has two types of users: the consumers that use the API in this package and the providers that implement the API in this package.
Example import for consumers using the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.log; version="[1.5,2.0)"
Example import for providers implementing the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.log; version="[1.5,1.6)"
-
FormatterLogger- Provides methods for bundles to write messages to the log using printf-style format strings. -
LogEntry- Provides methods to access the information contained in an individual Log Service log entry. -
Logger- Provides methods for bundles to write messages to the log using SLF4J-style format strings. -
LoggerConsumer- An operation that accepts a Logger argument and produces no result. -
LoggerFactory- Logger Factory service for logging information. -
LogLevel- Log Levels. -
LogListener- Subscribes toLogEntryobjects from theLogReaderService. -
LogReaderService- LogReaderService for obtaining logging information. -
LogService- LogService for logging information.
Provides methods for bundles to write messages to the log using printf-style format strings.
Messages can be formatted by the Logger once the Logger determines the log level is enabled. Uses printf-style format strings as described in java.util.Formatter.
You can also add a Throwable and/or ServiceReference to the
generated LogEntry by passing them to the logging methods as
additional arguments. If the last argument is a Throwable or
ServiceReference, it is added to the generated LogEntry and
then if the next to last argument is a ServiceReference or
Throwable and not the same type as the last argument, it is also
added to the generated LogEntry. These arguments will not be used as
message arguments. For example:
logger.info("Found service %s.", serviceReference, serviceReference);
logger.warn("Something named %s happened.", name, serviceReference,
throwable);
logger.error("Failed.", exception);If an exception occurs formatting the message, the logged message will indicate the formatting failure including the format string and the arguments.
1.4
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
Provides methods to access the information contained in an individual Log Service log entry.
A LogEntry object may be acquired from the
LogReaderService.getLog method or by registering a
LogListener object.
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
Returns the bundle that created this LogEntry object.
The bundle that created this LogEntry object;
null if no bundle is associated with this
LogEntry object.
Returns the exception object associated with this LogEntry
object.
In some implementations, the returned exception may not be the original exception. To avoid references to a bundle defined exception class, thus preventing an uninstalled bundle from being garbage collected, the Log Service may return an exception object of an implementation defined Throwable subclass. The returned object will attempt to provide as much information as possible from the original exception object such as the message and stack trace.
Throwable object of the exception associated with this
LogEntry;null if no exception is associated with
this LogEntry object.
Returns the integer level of this LogEntry object.
If one of the log methods of LogService was used, this is
the specified integer level. Otherwise, this is the
ordinal value of the log
level.
Integer level of this LogEntry object.
Since 1.4. Replaced by getLogLevel().
Returns the location information of the creation of this LogEntry
object.
The location information of the creation of this LogEntry
object.
1.4
Returns the name of the Logger object used to create this
LogEntry object.
The name of the Logger object used to create this
LogEntry object.
1.4
Returns the level of this LogEntry object.
The level of this LogEntry object.
1.4
Returns the formatted message associated with this LogEntry
object.
String containing the formatted message associated with
this LogEntry object.
Returns the sequence number for this LogEntry object.
A unique, non-negative value that is larger than all previously assigned values since the log implementation was started. These values are transient and are reused upon restart of the log implementation.
The sequence number for this LogEntry object.
1.4
Returns the ServiceReference object for the service associated
with this LogEntry object.
ServiceReference object for the service associated with
this LogEntry object; null if no
ServiceReference object was provided.
Returns a string representing the thread which created this
LogEntry object.
This string must contain the name of the thread and may contain other information about the thread.
A string representing the thread which created this
LogEntry object.
1.4
Provides methods for bundles to write messages to the log using SLF4J-style format strings.
Messages can be formatted by the Logger once the Logger determines the log
level is enabled. Use a left curly bracket ('{' \u007B)
followed by a right curly bracket ('}' \u007D) as a place
holder for an argument: "{}". If you need to use the literal
"{}" in the formatted message, precede the place holder with a
reverse solidus ('\' \u005C): "\{}". If you need to
place a backslash before the place holder, precede the reverse solidus with a
reverse solidus: "\\{}".
You can also add a Throwable and/or ServiceReference to the
generated LogEntry by passing them to the logging methods as
additional arguments. If the last argument is a Throwable or a
ServiceReference, it is added to the generated LogEntry and
then, if the next to last argument is a ServiceReference or
Throwable and not the same type as the last argument, it is also
added to the generated LogEntry. These arguments will not be used as
message arguments. For example:
logger.info("Found service {}.", serviceReference, serviceReference);
logger.warn("Something named {} happened.", name, serviceReference,
throwable);
logger.error("Failed.", exception);1.4
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
The message to log.
Log a message at the LogLevel.AUDIT level.
The format of the message to log.
The argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.AUDIT level.
The format of the message to log.
The first argument to format into the message.
The second argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.AUDIT level.
The format of the message to log.
The arguments to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.AUDIT level.
The message to log.
Log a message at the LogLevel.DEBUG level.
The format of the message to log.
The argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.DEBUG level.
The format of the message to log.
The first argument to format into the message.
The second argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.DEBUG level.
The format of the message to log.
The arguments to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.DEBUG level.
<E extends Exception>
The operation to perform on this Logger.
Perform the specified operation if logging enabled for the LogLevel.DEBUG level.
E– An exception thrown by the operation.
The message to log.
Log a message at the LogLevel.ERROR level.
The format of the message to log.
The argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.ERROR level.
The format of the message to log.
The first argument to format into the message.
The second argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.ERROR level.
The format of the message to log.
The arguments to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.ERROR level.
<E extends Exception>
The operation to perform on this Logger.
Perform the specified operation if logging enabled for the LogLevel.ERROR level.
E– An exception thrown by the operation.
The message to log.
Log a message at the LogLevel.INFO level.
The format of the message to log.
The argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.INFO level.
The format of the message to log.
The first argument to format into the message.
The second argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.INFO level.
The format of the message to log.
The arguments to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.INFO level.
<E extends Exception>
The operation to perform on this Logger.
Perform the specified operation if logging enabled for the LogLevel.INFO level.
E– An exception thrown by the operation.
Is logging enabled for the LogLevel.DEBUG level?
true if logging is enabled for the LogLevel.DEBUG
level.
Is logging enabled for the LogLevel.ERROR level?
true if logging is enabled for the LogLevel.ERROR
level.
Is logging enabled for the LogLevel.INFO level?
true if logging is enabled for the LogLevel.INFO
level.
Is logging enabled for the LogLevel.TRACE level?
true if logging is enabled for the LogLevel.TRACE
level.
Is logging enabled for the LogLevel.WARN level?
true if logging is enabled for the LogLevel.WARN
level.
The message to log.
Log a message at the LogLevel.TRACE level.
The format of the message to log.
The argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.TRACE level.
The format of the message to log.
The first argument to format into the message.
The second argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.TRACE level.
The format of the message to log.
The arguments to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.TRACE level.
<E extends Exception>
The operation to perform on this Logger.
Perform the specified operation if logging enabled for the LogLevel.TRACE level.
E– An exception thrown by the operation.
The message to log.
Log a message at the LogLevel.WARN level.
The format of the message to log.
The argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.WARN level.
The format of the message to log.
The first argument to format into the message.
The second argument to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.WARN level.
The format of the message to log.
The arguments to format into the message.
Log a formatted message at the LogLevel.WARN level.
<E extends Exception>
The operation to perform on this Logger.
Perform the specified operation if logging enabled for the LogLevel.WARN level.
E– An exception thrown by the operation.
The type of the exception that may be thrown.
An operation that accepts a Logger argument and produces no result.
This is a functional interface and can be used as the assignment target for a lambda expression or method reference.
1.4
Thread-safe
Logger Factory service for logging information.
Provides methods for bundles to obtain named Loggers that can be used to write messages to the log.
Logger names should be in the form of a fully qualified Java class names with
segments separated by full stop ('.' \u002E). For example:
com.foo.Bar
Logger names exist in a hierarchy. A logger name is said to be an ancestor of
another logger name if the logger name followed by a full stop ('.'
\u002E) is a prefix of the descendant logger name. The
root logger name is the top ancestor of the
logger name hierarchy. For example:
com.foo.Bar
com.foo
com
ROOT1.4
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
The name to use for the logger name. Must not be
null.
Return the Logger named with the specified name.
The Logger named with the specified name. If the name parameter is equal to Logger.ROOT_LOGGER_NAME, then the root logger is returned.
The class to use for the logger name. Must not be
null.
Return the Logger named with the specified class.
The Logger named with the name of the specified class.
<L extends Logger>
The Logger type.
The name to use for the logger name. Must not be
null.
The type of Logger. Can be Logger or FormatterLogger.
Return the Logger of the specified type named with the specified name.
The Logger or FormatterLogger named with the specified name. If the name parameter is equal to Logger.ROOT_LOGGER_NAME, then the root logger is returned.
IllegalArgumentException– If the specified type is not a supported
Logger type.
<L extends Logger>
A Logger type.
The class to use for the logger name. Must not be
null.
The type of Logger. Can be Logger or
FormatterLogger. Must not be null.
Return the Logger of the specified type named with the specified class.
The Logger or FormatterLogger named with the name of the specified class.
IllegalArgumentException– If the specified type is not a supported
Logger type.
<L extends Logger>
The Logger type.
The bundle associated with the Logger. Must not be
null.
The name to use for the logger name. Must not be
null.
The type of Logger. Can be Logger or
FormatterLogger. Must not be null.
Return the Logger of the specified type named with the specified name for the specified bundle.
This method is not normally used. The other getLogger methods
return a Logger associated with the bundle used to obtain this
Logger Factory service. This method is used to obtain a Logger
for the specified bundle which may be useful to code which is logging on
behalf of another bundle.
The Logger or FormatterLogger named with the specified name for the specified bundle. If the name parameter is equal to Logger.ROOT_LOGGER_NAME, then the root logger is returned.
IllegalArgumentException– If the specified type is not a supported
Logger type or the specified Bundle is not a resolved bundle.
Log Levels.
1.4
The other log level.
Returns whether this log level implies the specified log level.
true If this log level implies the specified log level;
false otherwise.
Subscribes to LogEntry objects from the LogReaderService.
A LogListener object may be registered with the Log Reader Service
using the LogReaderService.addLogListener method. After the listener
is registered, the logged method will be called for each
LogEntry object created. The LogListener object may be
unregistered by calling the LogReaderService.removeLogListener
method.
Since 1.4, org.osgi.service.log.stream.LogStreamProvider is the preferred way to obtain LogEntry objects.
Thread-safe
A LogEntry object containing log information.
Listener method called for each LogEntry object created.
LogReaderService for obtaining logging information.
Since 1.4, org.osgi.service.log.stream.LogStreamProvider is the preferred way to obtain LogEntry objects.
The LogReaderService provides two ways to obtain LogEntry objects:
-
The primary way to retrieve LogEntry objects is to register a LogListener object whose LogListener.logged(LogEntry) method will be called for each entry added to the log.
-
To obtain past LogEntry objects, the getLog() method can be called which will return an
Enumerationof the LogEntry objects in the log.
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
A LogListener object to register; the LogListener object is used to receive LogEntry objects.
Subscribes to LogEntry objects.
This method registers a LogListener object with the Log Reader Service. The LogListener.logged(LogEntry) method will be called for each LogEntry object placed into the log.
When a bundle which registers a LogListener object is stopped or otherwise releases the Log Reader Service, the Log Reader Service must remove all of the bundle's listeners.
If this Log Reader Service's list of listeners already contains a
listener l such that (l==listener), this method does
nothing.
Since 1.4, org.osgi.service.log.stream.LogStreamProvider is the preferred way to obtain LogEntry objects.
Returns an Enumeration of the LogEntry objects in the
log.
Each element of the enumeration is a LogEntry object, ordered with the most recent entry first. Whether the enumeration is of all LogEntry objects since the Log Service was started or some recent past is implementation-specific.
An Enumeration of the LogEntry objects in the
log.
A LogListener object to unregister.
Unsubscribes to LogEntry objects.
This method unregisters a LogListener object from the Log Reader Service.
If listener is not contained in this Log Reader Service's list of
listeners, this method does nothing.
Since 1.4, org.osgi.service.log.stream.LogStreamProvider is the preferred way to obtain LogEntry objects.
LogService for logging information.
Replaced by LoggerFactory.
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
A debugging message (Value 4).
This log entry is used for problem determination and may be irrelevant to anyone but the bundle developer.
Since 1.4. Replaced by LogLevel.DEBUG.
An error message (Value 1).
This log entry indicates the bundle or service may not be functional.
Since 1.4. Replaced by LogLevel.ERROR.
An informational message (Value 3).
This log entry may be the result of any change in the bundle or service and does not indicate a problem.
Since 1.4. Replaced by LogLevel.INFO.
A warning message (Value 2).
This log entry indicates a bundle or service is still functioning but may experience problems in the future because of the warning condition.
Since 1.4. Replaced by LogLevel.WARN.
The severity of the message. This should be one of the defined log levels but may be any integer that is interpreted in a user defined way.
Human readable string describing the condition or
null.
Logs a message.
The ServiceReference field and the Throwable field of the
LogEntry object will be set to null.
This method will log to the bundle's Logger named
"LogService.<bsn>" where <bsn> is the Bundle Symbolic
Name of the bundle.
The specified level is mapped to a LogLevel as follows:
-
Any other value - LogLevel.TRACE
In the generated log entry, LogEntry.getLevel() must return the specified level.
Since 1.4. Replaced by Logger. See LoggerFactory.
The severity of the message. This should be one of the defined log levels but may be any integer that is interpreted in a user defined way.
The human readable string describing the condition or
null.
The exception that reflects the condition or
null.
Logs a message with an exception.
The ServiceReference field of the LogEntry object will be
set to null.
This method will log to the bundle's Logger named
"LogService.<bsn>" where <bsn> is the Bundle Symbolic
Name of the bundle.
The specified level is mapped to a LogLevel as follows:
-
Any other value - LogLevel.TRACE
In the generated log entry, LogEntry.getLevel() must return the specified level.
Since 1.4. Replaced by Logger. See LoggerFactory.
The ServiceReference object of the service that this
message is associated with or null.
The severity of the message. This should be one of the defined log levels but may be any integer that is interpreted in a user defined way.
Human readable string describing the condition or
null.
Logs a message associated with a specific ServiceReference
object.
The Throwable field of the LogEntry will be set to
null.
This method will log to the bundle's Logger named
"LogService.<bsn>" where <bsn> is the Bundle Symbolic
Name of the bundle.
The specified level is mapped to a LogLevel as follows:
-
Any other value - LogLevel.TRACE
In the generated log entry, LogEntry.getLevel() must return the specified level.
Since 1.4. Replaced by Logger. See LoggerFactory.
The ServiceReference object of the service that this
message is associated with.
The severity of the message. This should be one of the defined log levels but may be any integer that is interpreted in a user defined way.
Human readable string describing the condition or
null.
The exception that reflects the condition or
null.
Logs a message with an exception associated and a
ServiceReference object.
This method will log to the bundle's Logger named
"LogService.<bsn>" where <bsn> is the Bundle Symbolic
Name of the bundle.
The specified level is mapped to a LogLevel as follows:
-
Any other value - LogLevel.TRACE
In the generated log entry, LogEntry.getLevel() must return the specified level.
Since 1.4. Replaced by Logger. See LoggerFactory.
Log Admin Package Version 1.0.
Bundles wishing to use this package must list the package in the Import-Package header of the bundle's manifest. This package has two types of users: the consumers that use the API in this package and the providers that implement the API in this package.
Example import for consumers using the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.log.admin; version="[1.0,2.0)"
Example import for providers implementing the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.log.admin; version="[1.0,1.1)"
-
LoggerAdmin- LoggerAdmin service for configuring loggers. -
LoggerContext- Logger Context for a bundle.
LoggerAdmin service for configuring loggers.
Each bundle may have its own named LoggerContext based upon its bundle symbolic name, bundle version, and bundle location. There is also a root Logger Context from which each named Logger Context inherits. The root Logger Context has no name.
When a bundle logs, the logger implementation must locate the Logger Context for the bundle to determine the effective log level of the logger name. The best matching name for the Logger Context is the longest name, which has a non-empty Logger Context, according to this syntax:
name ::= symbolic-name ( '|' version ( '|' location )? )?
The version must be formatted canonically, that is, according to the
toString() method of the Version class. So the Logger Context
for a bundle is searched for using the following names in the given order:
<symbolic-name>|<version>|<location>
<symbolic-name>|<version>
<symbolic-name>The search stops at the first non-empty Logger Context. If no non-empty Logger Context is found using the above search order, the Logger Context with the symbolic name of the bundle must be used for the bundle.
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
Logger Admin service property to associate the Logger Admin service with a LoggerFactory service.
This service property is set to the service.id for the
LoggerFactory service administered by this Logger Admin.
The value of this service property must be of type Long.
The name of the Logger Context. Can be null to
specify the root Logger Context.
Get the Logger Context for the specified name.
The Logger Context for the specified name. The returned Logger Context may be empty.
Logger Context for a bundle.
Any change to the configuration of this Logger Context must be effective immediately for all loggers that would rely upon the configuration of this Logger Context.
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
Framework launching property specifying the default log level of the root Logger Context.
The value of this property must be the name of the one of the LogLevels.
If not specified, or the specified value is not the name of the one of the LogLevels, the default log level of the root Logger Context is LogLevel.WARN.
Logger Context PID.
If Configuration Admin is present, Logger Context configuration information in Configuration Admin must be used. The name of the Logger Context is mapped to a Configuration Admin targeted PID as follows:
-
The root Logger Context, which has no name, is mapped to the PID
org.osgi.service.log.admin. -
A named Logger Context is mapped to a targeted PID by prefixing the Logger Context's name with
org.osgi.service.log.adminfollowed by vertical line ('|'\u007c). For example, the Logger Context namedcom.foo.baris mapped to the targeted PIDorg.osgi.service.log.admin|com.foo.bar.
Clear the configuration of this Logger Context.
The configured log levels will be cleared.
The logger name.
Returns the effective log level of the logger name in this Logger Context.
The effective log level for a logger name is found by the following steps:
-
If the specified logger name is configured with a log level, return the configured log level.
-
For each ancestor logger name of the specified logger name, if the ancestor logger name is configured with a log level, return the configured log level.
-
If this Logger Context is named, return the result of calling this method on the root Logger Context with the specified logger name.
-
If this Logger Context is the root Logger Context, return the default log level of the root Logger Context.
The effective log level of the logger name in this Logger Context.
Returns the configured log levels for this Logger Context.
The configured log levels for this Logger Context. The keys are the logger names and the values are the log levels. The returned map may be empty if no logger names are configured for this Logger Context. The returned map is the property of the caller who can modify the map and use it as input to setLogLevels(Map). The returned map must support all optional Map operations.
Returns the name for this Logger Context.
The name for this Logger Context. The root Logger Context has no
name and returns null.
Returns whether the configuration of this Logger Context is empty.
true if this Logger Context has no configuration. That
is, the configured log levels are empty. Otherwise false
is returned.
The log levels to configure for this Logger Context. The keys are the logger names and the values are the log levels. The specified map is the property of the caller and this method must not modify or retain the specified map.
Configure the log levels for this Logger Context.
All previous log levels configured for this Logger Context are cleared and then the log levels in the specified map are configured.
The configured log levels for this Logger Context can be set by both this method and by configuration information in Configuration Admin, if Configuration Admin is present. The configured log levels for this Logger Context are based upon the last technique used to update the configured log levels. This method must not modify or set configuration information in Configuration Admin.
[1]SLF4Jhttps://www.slf4j.org